Hibernate is a OR-mapped Java persistence framework which not only takes care of the mapping from Java classes to database tables, but also provides data query and retrieval facilities. In a previous article, I’ve explained how to integrate a Hibernate minimal configuration in a Struts MVC web application.
Now I will show how to add an advanced Hibernate persistence implementation using the DAO and Factory design patterns from the CaveatEmptor example application. This solution combines both the Factory and the DAO design patterns:
– Factory pattern, creates object without exposing the creation logic to the client and refers to newly created object using a common interface.
– Data Access Object Pattern or DAO pattern is used to separate low level data accessing API or operations from high level business services .
This approach provides higher abstraction to the persistence layer of a web application. Here a high level class diagram.
Let’s start with the DAO pattern. We add the abstract factory and the concrete factory for Hibernate DAOs.
– DAOFactory
package com.demo.hibernate;
public abstract class DAOFactory {
/**
* Creates a standalone DAOFactory that returns unmanaged DAO
* beans for use in any environment Hibernate has been configured
* for. Uses HibernateUtil/SessionFactory and Hibernate context
* propagation (CurrentSessionContext), thread-bound or transaction-bound,
* and transaction scoped.
*/
public static final Class HIBERNATE = DAOHibernateFactory.class;
/**
* Factory method for instantiation of concrete factories.
*/
public static DAOFactory instance(Class factory) {
try {
return (DAOFactory)factory.newInstance();
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Couldn't create DAOFactory: " + factory);
}
}
// Add your DAO interfaces here
}
– DAOHibernateFactory
package com.demo.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
public class DAOHibernateFactory extends DAOFactory {
private GenericHibernateDAO instantiateDAO(Class daoClass) {
try {
GenericHibernateDAO dao = (GenericHibernateDAO)daoClass.newInstance();
dao.setSession(getCurrentSession());
return dao;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can not instantiate DAO: " + daoClass, ex);
}
}
// You could override this if you don't want HibernateUtil for lookup
protected Session getCurrentSession() {
return SessionUtil.getSessionFactory().getCurrentSession();
}
}
We continue with the GenericDAO interface and its implementation for common CRUD functionality
– GenericDAO
package com.demo.hibernate;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
public interface GenericDAO<T, ID extends Serializable> {
T findById(ID id, boolean lock);
List<T> findAll();
List<T> findByExample(T exampleInstance, String[] excludeProperty);
T makePersistent(T entity);
void makeTransient(T entity);
}
– GenericHibernateDAO
package com.demo.hibernate;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.LockMode;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Criterion;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Example;
public abstract class GenericHibernateDAO<T, ID extends Serializable> implements GenericDAO<T, ID> {
private Class<T> persistentClass;
private Session session;
public GenericHibernateDAO() {
this.persistentClass = (Class<T>) ((ParameterizedType) getClass().getGenericSuperclass()).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void setSession(Session s) {
this.session = s;
}
protected Session getSession() {
if (session == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Session has not been set on DAO before usage");
return session;
}
public Class<T> getPersistentClass() {
return persistentClass;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T findById(ID id, boolean lock) {
T entity;
if (lock)
//entity = (T) getSession().load(getPersistentClass(), id, LockMode.UPGRADE);
entity = (T) getSession().get(getPersistentClass(), id, LockMode.UPGRADE);
else
//entity = (T) getSession().load(getPersistentClass(), id);
entity = (T) getSession().get(getPersistentClass(), id);
return entity;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public List<T> findAll() {
return findByCriteria();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public List<T> findByExample(T exampleInstance, String[] excludeProperty) {
Criteria crit = getSession().createCriteria(getPersistentClass());
Example example = Example.create(exampleInstance);
for (String exclude : excludeProperty) {
example.excludeProperty(exclude);
}
crit.add(example);
return crit.list();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T makePersistent(T entity) {
getSession().saveOrUpdate(entity);
return entity;
}
public void makeTransient(T entity) {
getSession().delete(entity);
}
public void flush() {
getSession().flush();
}
public void clear() {
getSession().clear();
}
}
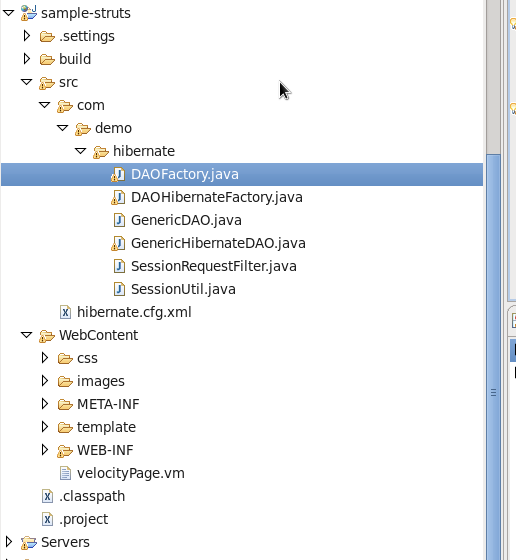
Here is the project layout
 English
English Italian
Italian