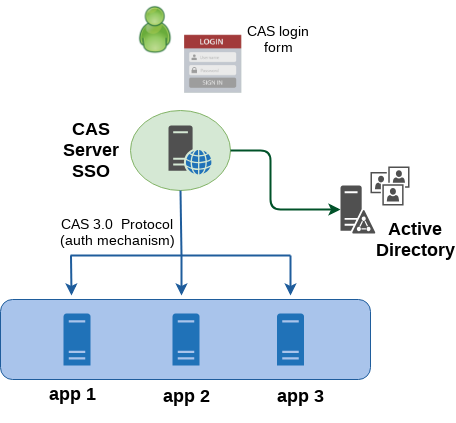
Ecco un pratico esempio di come integrare Apereo CAS con una o più applicazioni web scritte in Java che utilizzano Spring Security. Il risultato è un web Single-Sign On centralizzato che vede CAS come unico sistema di controllo degli accessi e che consente perciò agli utenti di poter fruire di più risorse protette, effettuando un’unica autenticazione. In questo esempio, la comunicazione tra il CAS server e le applicazioni web protette, anche chiamate CAS client o CAS service, è ticket-based ed è implementata su protocollo CAS 3.0 (altri protocolli supportati da CAS sono SAML, OpenID, OAuth). L’immagine seguente mostra una visione ad alto livello dell’architettura del sistema.
Stack
- Apereo CAS 5.2.3
- Spring Security 5.0.3.RELEASE
- Spring MVC 5.0.3.RELEASE
- LDAP Active Directory 2012
- JDK 1.8.0_112
- Maven 3.5.0
NOTE: Il codice sorgente trattato in questo articolo si trova nella directory mvc-security-cas
CAS Server Setup
Scaricare il sorgente di CAS server dal repository git e abilitare un handler di autenticazione. In questo esempio ho integrato CAS a un server Active Directory con degli utenti di test, per cui è sufficiente aggiungere la dipendenza al supporto LDAP nel pom.xml del sorgente.
$ git clone https://github.com/apereo/cas-overlay-template.git
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apereo.cas</groupId>
<artifactId>cas-server-support-ldap</artifactId>
<version>${cas.version}</version>
</dependency>
Per definire le webapp che sono protette da CAS utilizzerò un file JSON ma è necessario anche in questo caso aggiungere nel pom.xml la dipendenza a json-service-registry per la definizione dei servizi in formato json
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apereo.cas</groupId>
<artifactId>cas-server-support-json-service-registry</artifactId>
<version>${cas.version}</version>
</dependency>
Il nome del file json che definisce i servizi deve essere creato secondo la convenzione segueente:
## ./cas-server/src/main/cas-server-config/client-services/appA-100.json
{
"@class" : "org.apereo.cas.services.RegexRegisteredService",
"serviceId" : "http://localhost:9090/appA.*",
"name" : "appA",
"id" : 100,
"evaluationOrder" : 1
}
## ./cas-server/src/main/cas-server-config/client-services/appB-200.json
{
"@class" : "org.apereo.cas.services.RegexRegisteredService",
"serviceId" : "http://localhost:9090/appB.*",
"name" : "appB",
"id" : 200,
"evaluationOrder" : 1
}
Assicurarsi che CAS sia in esecuzione su HTTPS altrimenti la funzionalità di SSO non funzionerà. La pagina di login di CAS mostra un warning di questo tipo:
In order to have SSO on work, you must log in over HTTPS.
## src/main/cas-server-config/cas.properties
## CAS on HTTPS
##
server.context-path=/cas
cas.server.name=https://localhost:8443
cas.server.prefix=https://localhost:8443/cas
# These properties have impacts only on the embedded Tomcat server
server.ssl.enabled=true
server.port=8443
server.ssl.key-store=file:/home/user/cas-certs/cas.keystore
server.ssl.key-store-password=store12345
server.ssl.key-password=key12345
## SERVICES REGISTRY
##
cas.serviceRegistry.initFromJson=false
cas.serviceRegistry.json.location=file:/home/user/project/src/main/cas-server-config/client-services
## LDAP AUTHENTICATION
##
cas.authn.ldap[0].type=AD
cas.authn.ldap[0].ldapUrl=ldap://192.168.56.120:389
cas.authn.ldap[0].useSsl=false
cas.authn.ldap[0].baseDn=OU=test-foo,DC=example,DC=com
cas.authn.ldap[0].bindDn=CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com
cas.authn.ldap[0].bindCredential=12345
cas.authn.ldap[0].userFilter=sAMAccountName={user}
cas.authn.ldap[0].dnFormat=%s@example.com
cas.authn.ldap[0].principalAttributeId=sAMAccountName
CAS Client Setup
La webapp di questo esempio utilizza Spring MVC e Spring Security che fornisce nativamente supporto all’integrazione con CAS. Basta aggiungere la dipendenza dal modulo nel pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-cas</artifactId>
</dependency>
Per inizializzare l’application context, utilizzo un’implementazione di Spring WebApplicationInitializer. Questo mi consente di istanziare programmaticamente filtri, servlet, e listener direttamente in Java senza utilizzare il tradizionale approccio via web.xml.
// Creating the servlet application context by using annotation based context
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
webApplicationContext.register(MvcConfigurer.class);
webApplicationContext.register(CasConfigurer.class);
webApplicationContext.register(SecurityConfigurer.class);
webApplicationContext.setServletContext(servletContext);
// Spring DelegatingFilterProxy which allows you to enable Spring Security and use your custom Filters
FilterRegistration.Dynamic filterRegistration = servletContext.addFilter("giusWebappFilterDelegator", new DelegatingFilterProxy("springSecurityFilterChain"));
filterRegistration.addMappingForUrlPatterns(null, false, "/*");
La definizione di tutti gli oggetti legati a CAS viene fatta via annotation. Lo scopo della classe CasConfigurer è proprio quello di centralizzare tutte le configurazioni di CAS in un’unico oggetto.
/**
* CAS global properties.
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ServiceProperties serviceProperties() {
String appLogin = "http://localhost:18080/mvc-casclient/login-cas";
ServiceProperties serviceProperties = new ServiceProperties();
serviceProperties.setService(appLogin);
serviceProperties.setAuthenticateAllArtifacts(true);
return serviceProperties;
}
/**
* The entry point of Spring Security authentication process (based on CAS).
* The user's browser will be redirected to the CAS login page.
* @return
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationEntryPoint casAuthenticationEntryPoint() {
String casLogin = "https://localhost:8443/cas/login";
CasAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new CasAuthenticationEntryPoint();
entryPoint.setLoginUrl(casLogin);
entryPoint.setServiceProperties(serviceProperties());
return entryPoint;
}
/**
* CAS ticket validator, if you plan to use CAS 3.0 protocol
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Cas30ServiceTicketValidator ticketValidatorCas30() {
Cas30ServiceTicketValidator ticketValidator = new Cas30ServiceTicketValidator("http://localhost:8080/cas");
return ticketValidator;
}
/**
* The authentication provider that integrates with CAS.
* This implementation uses CAS 3.0 protocol for ticket validation.
*
*/
@Bean
public CasAuthenticationProvider casAuthenticationProvider() {
CasAuthenticationProvider provider = new CasAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setServiceProperties(serviceProperties());
provider.setTicketValidator(ticketValidatorCas30());
// Loads only a default set of authorities for any authenticated users (username and password are)
provider.setUserDetailsService((UserDetailsService) fakeUserDetailsService());
provider.setKey("CAS_PROVIDER_KEY_LOCALHOST");
return provider;
}
/**
* CAS Authentication Provider does not use credentials specified here for authentication. It only loads
* the authorities for a user, once they have been authenticated by CAS.
*
*/
@Bean
public User fakeUserDetailsService(){
return new User("fakeUser", "fakePass", true, true, true, true, AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("ROLE_USER"));
}
SecurityConfigurer estende Spring WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter e inizializza Spring Security.
// Let Spring resolves and injects collaborating beans into this class by @Autowired annotations...
@Autowired
private AuthenticationProvider casAuthenticationProvider;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPoint casAuthenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private ServiceProperties casServiceProperties;
/**
* Configures web based security for specific http requests.
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
http.httpBasic()
.authenticationEntryPoint(casAuthenticationEntryPoint);
http.addFilter(casAuthenticationFilter());
}
/**
* Configures multiple Authentication providers.
* AuthenticationManagerBuilder allows for easily building multiple authentication mechanisms in the order they're declared.
* CasAuthenticationProvider is used here.
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(casAuthenticationProvider);
}
/**
* Cas authentication filter responsible processing a CAS service ticket.
* Here, I was unable to declare this bean in the Cas configurator class( https://tinyurl.com/y9fzgma9 )
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
public CasAuthenticationFilter casAuthenticationFilter() throws Exception {
CasAuthenticationFilter filter = new CasAuthenticationFilter();
filter.setServiceProperties(casServiceProperties);
filter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager());
return filter;
}
Il controller gestisce le url per le richieste verso la pagina di login dell’applicazione “/sso-login” e il redirect alla root web context “/”
@GetMapping("/sso-login")
public String login(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "redirect:/";
}
@RequestMapping(value = {"/"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView defaultView (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String pageName = "index.html";
ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView(pageName);
return view;
}
 Italiano
Italiano Inglese
Inglese